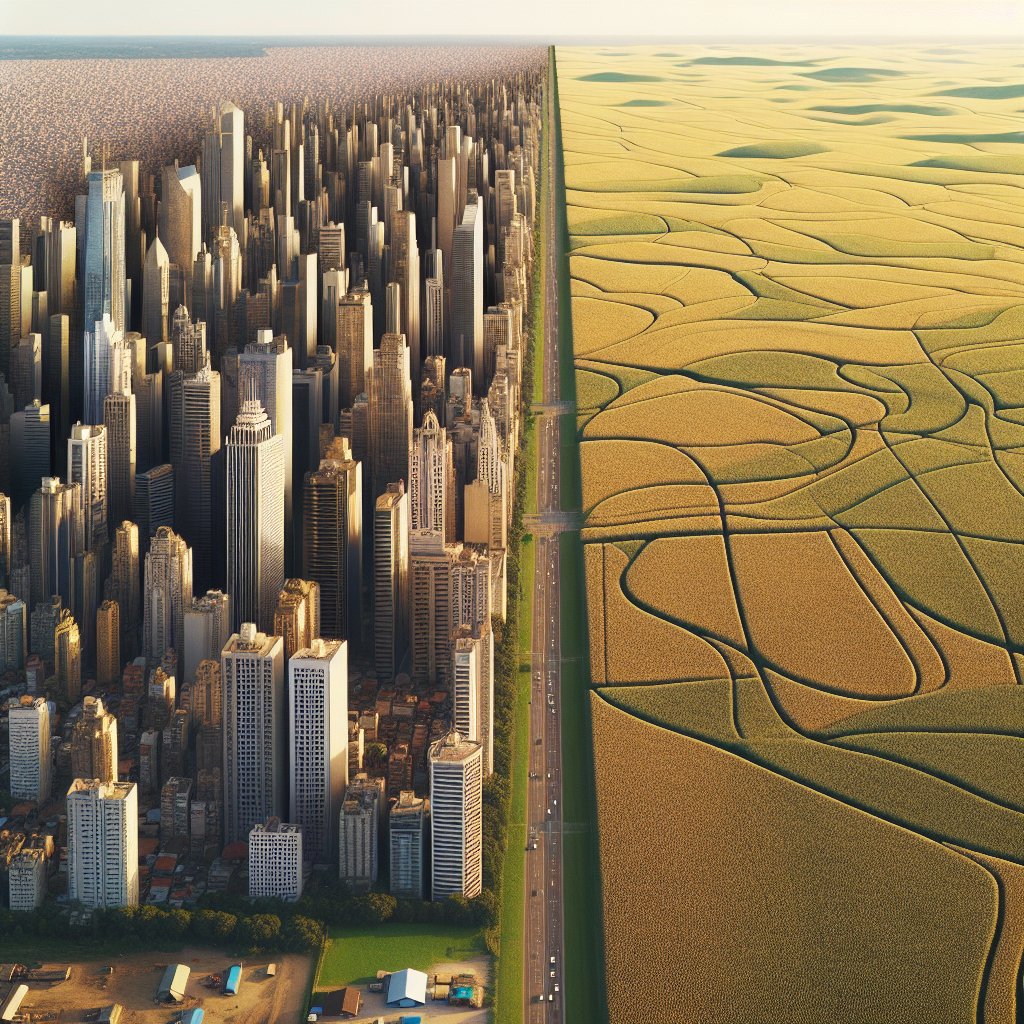
Urban sprawl significantly influences grain farming, reshaping agricultural landscapes and practices. As cities expand, the encroachment on arable land poses challenges for farmers, affecting everything from crop production to market access. This article delves into the multifaceted relationship between urban development and grain farming, exploring the implications of urban sprawl on agricultural sustainability, economic viability, and food security.
Understanding Urban Sprawl
Urban sprawl refers to the uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into the surrounding rural land. This phenomenon is characterized by low-density development, reliance on automobiles, and a significant increase in land consumption. As cities grow, they often extend into agricultural zones, leading to the conversion of farmland into residential, commercial, and industrial spaces. The consequences of this transformation are profound, particularly for grain farming, which relies heavily on large tracts of land for cultivation.
The Drivers of Urban Sprawl
Several factors contribute to urban sprawl, including population growth, economic development, and changes in lifestyle preferences. As more people migrate to urban areas in search of better job opportunities and living conditions, the demand for housing increases. This demand often leads to the development of suburban neighborhoods, which can encroach upon valuable agricultural land.
- Population Growth: The continuous influx of people into cities creates pressure on housing and infrastructure, prompting expansion into surrounding areas.
- Economic Development: As economies grow, the need for commercial and industrial spaces rises, often at the expense of agricultural land.
- Changing Lifestyles: The desire for larger homes and green spaces drives people to seek properties in suburban areas, leading to further sprawl.
Consequences of Urban Sprawl on Grain Farming
The impact of urban sprawl on grain farming is multifaceted, affecting land availability, farming practices, and the overall agricultural economy. As urban areas expand, the following consequences become evident:
- Loss of Arable Land: One of the most immediate effects of urban sprawl is the reduction of available farmland. As cities grow, prime agricultural land is often converted into residential and commercial developments, leading to a decline in grain production capacity.
- Increased Land Prices: The encroachment of urban development drives up land prices, making it more difficult for farmers to acquire or maintain land for grain production. This economic pressure can lead to the consolidation of farms and the loss of small-scale farming operations.
- Fragmentation of Agricultural Land: Urban sprawl can result in the fragmentation of farmland, making it less efficient for farmers to operate. Smaller, disconnected plots of land can hinder the ability to use modern farming techniques and machinery effectively.
- Environmental Impact: The conversion of farmland to urban areas can lead to environmental degradation, including loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, and increased pollution. These factors can negatively affect the sustainability of grain farming practices.
Adapting to Change: Strategies for Grain Farmers
Despite the challenges posed by urban sprawl, grain farmers can adopt various strategies to adapt to the changing landscape. These strategies focus on enhancing productivity, sustainability, and resilience in the face of urban encroachment.
Innovative Farming Practices
To counteract the effects of urban sprawl, farmers can implement innovative farming practices that maximize productivity on smaller plots of land. Techniques such as vertical farming, hydroponics, and precision agriculture can help farmers increase yields while minimizing the environmental impact.
- Vertical Farming: This method involves growing crops in stacked layers, often in controlled indoor environments. Vertical farming can significantly increase crop yields per square foot, making it a viable option for urban areas.
- Hydroponics: Hydroponic systems allow farmers to grow crops without soil, using nutrient-rich water instead. This method can be particularly effective in urban settings where space is limited.
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing technology such as GPS and data analytics, precision agriculture enables farmers to optimize their use of resources, reducing waste and increasing efficiency.
Community Engagement and Advocacy
Grain farmers can also engage with their communities to advocate for policies that protect agricultural land from urban sprawl. By collaborating with local governments, agricultural organizations, and community groups, farmers can promote sustainable land-use practices and zoning regulations that prioritize the preservation of farmland.
- Land-Use Planning: Advocating for smart growth policies that prioritize the preservation of agricultural land can help mitigate the impacts of urban sprawl.
- Community Supported Agriculture (CSA): Farmers can establish CSA programs that connect them directly with consumers, fostering a sense of community and support for local agriculture.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of local grain farming and its role in food security can help garner public support for agricultural preservation efforts.
The Future of Grain Farming in Urbanized Areas
The future of grain farming in the context of urban sprawl will depend on the ability of farmers, policymakers, and communities to adapt to changing circumstances. As urban areas continue to expand, innovative solutions and collaborative efforts will be essential to ensure the sustainability of grain farming.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology will play a crucial role in shaping the future of grain farming. From improved crop varieties to automated farming equipment, technology can help farmers increase efficiency and productivity, even in the face of urban encroachment.
- Genetic Engineering: The development of genetically modified crops can lead to higher yields and greater resistance to pests and diseases, making grain farming more viable in urbanized areas.
- Automation: The use of drones, robotics, and automated machinery can streamline farming operations, allowing farmers to manage their land more effectively.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging big data can help farmers make informed decisions about crop management, resource allocation, and market trends.
Policy and Planning for Sustainable Agriculture
Effective policy and planning will be essential to support grain farming in the face of urban sprawl. Policymakers must prioritize agricultural land preservation and create incentives for sustainable farming practices.
- Incentives for Sustainable Practices: Providing financial incentives for farmers who adopt sustainable practices can encourage the preservation of farmland and promote environmentally friendly farming methods.
- Urban Agriculture Initiatives: Supporting urban agriculture initiatives can help integrate farming into urban environments, providing fresh produce to city dwellers while preserving agricultural land.
- Collaboration with Urban Planners: Engaging with urban planners to create land-use policies that balance development with agricultural needs can help protect farmland from encroachment.
Conclusion
The impact of urban sprawl on grain farming is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach. As cities continue to expand, the challenges faced by grain farmers will only intensify. However, through innovative practices, community engagement, and supportive policies, it is possible to create a sustainable future for grain farming in urbanized areas. By recognizing the value of agricultural land and working collaboratively, we can ensure that grain farming remains a vital component of our food system, even in the face of urban growth.